Overview
Seed-Coder is a research-first, open-source family of ~8B-parameter code-focused language models designed around a model-centric data curation pipeline. Instead of relying primarily on hand-written rules to filter pretraining code data, Seed-Coder uses large language models to score and filter candidate code (from GitHub, commits, and code-related web sources), aiming to capture nuanced signals of code quality that rule-based filters miss. The project releases base, instruct, and reasoning variants of the model family and emphasizes transparency, reproducibility, and strong benchmark performance across software-engineering and competitive-programming tasks. A Technical Report is referenced on the site for deeper results, though direct PDF links on the hosted pages appear broken or return 404s.
Key Features
Model-centric data curation
Uses LLMs to score and filter candidate pretraining code data (GitHub repositories, commits, code-related web data) rather than relying on hand-crafted rule sets.
Open-source 8B code model family
Provides base, instruct, and reasoning variants around ~8B parameters for different use-cases (pretraining base, instruction-following, and reasoning/CP tasks).
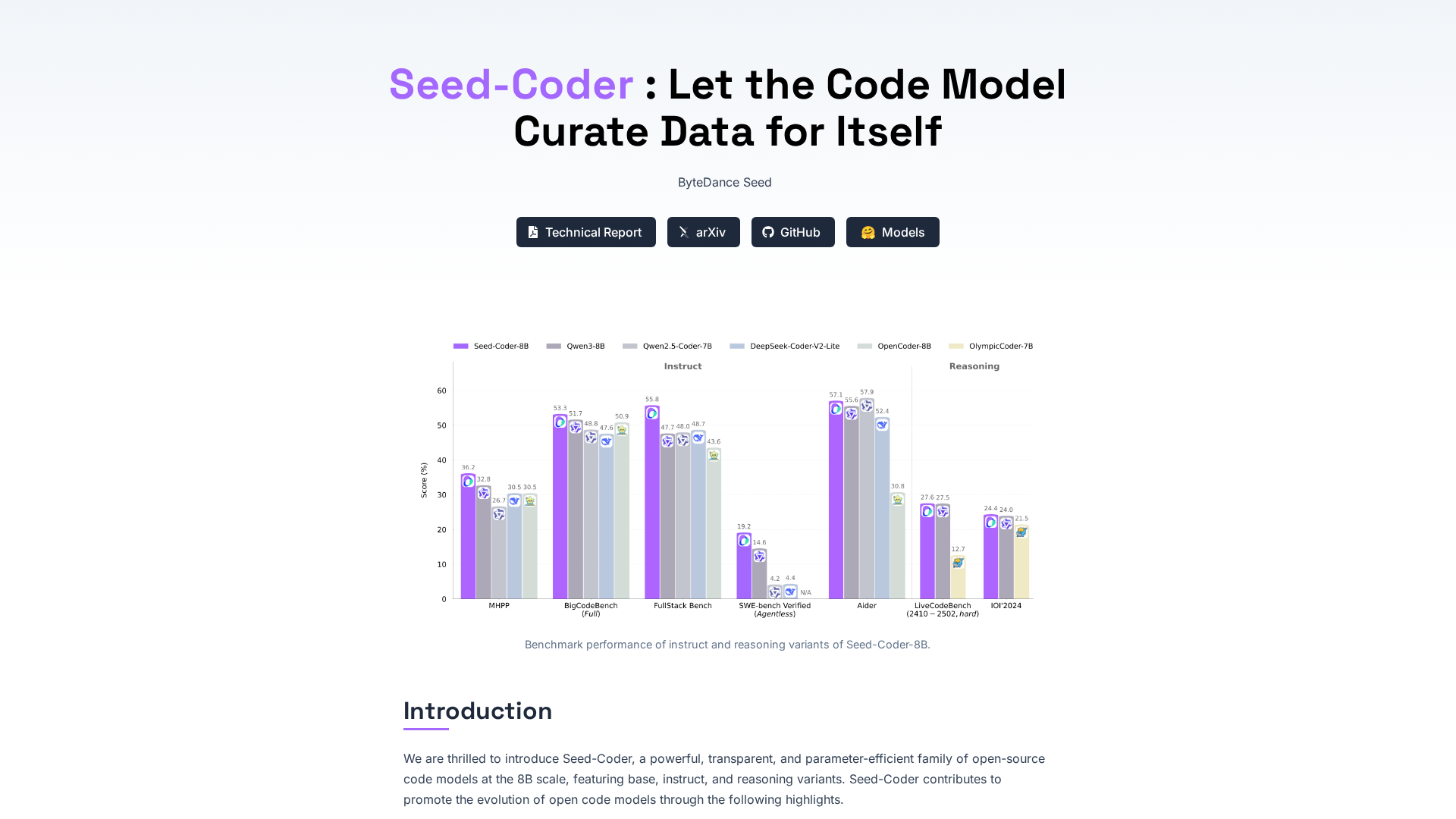
Benchmarked performance
Reported top results among ~8B models on SWE-bench Verified and Multi-SWE-bench mini; strong results on IOI’2024 and Codeforces ELO for reasoning variant.
Transparency and reproducibility
Project emphasizes transparency in data curation and research reporting; a Technical Report is referenced for deeper evaluation (PDF link currently not found on the hosted site).
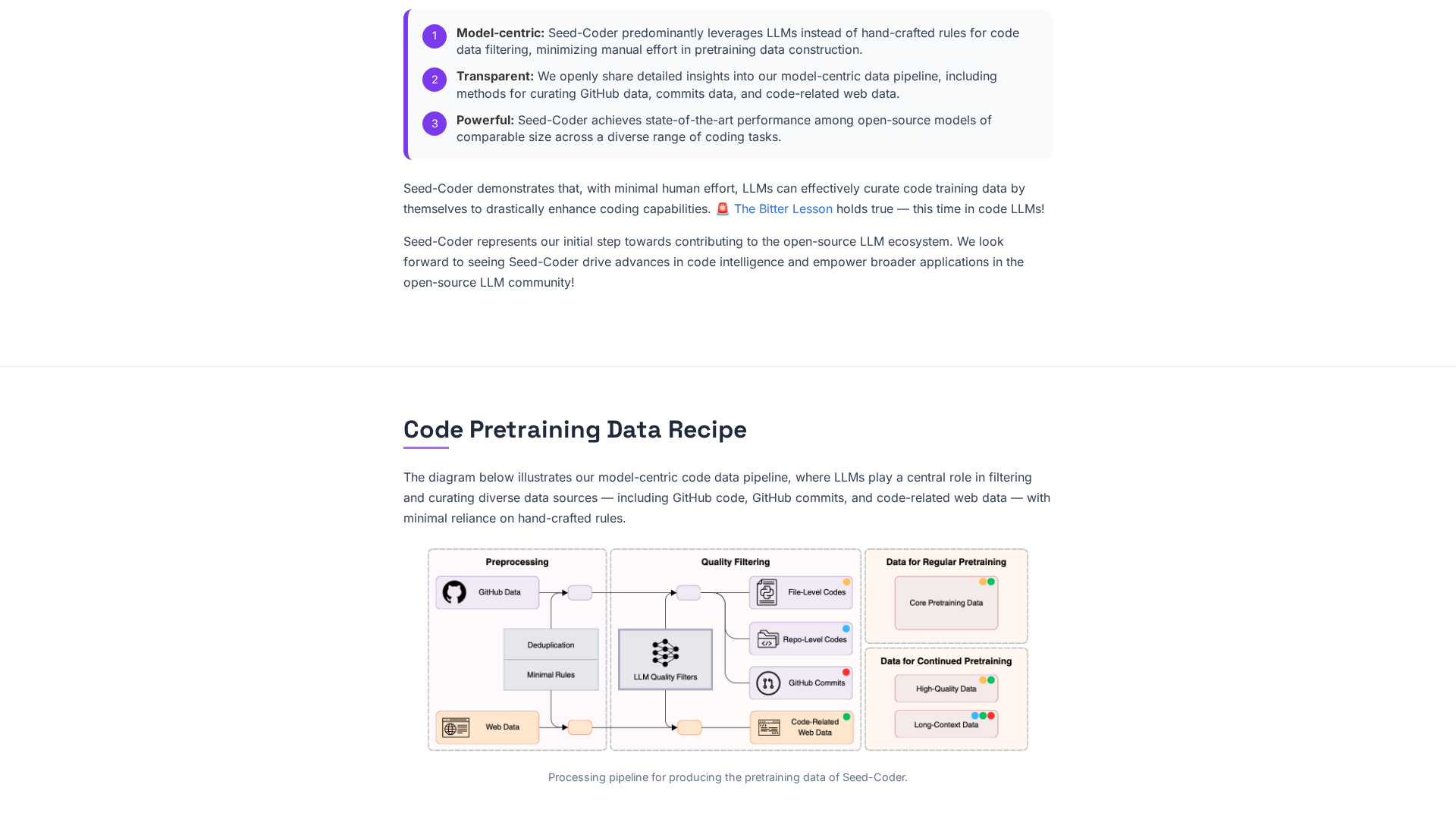
Pipeline sources and minimal manual rules
Data pipeline sources include GitHub code, commit history, and code-related web data; LLM filters reduce the need for hand-crafted cleaning rules.
Support for agentless workflows / OpenHands
Site mentions compatibility with agentless workflows and the OpenHands evaluation framework for benchmarking code models.
Who Can Use This Tool?
- Researchers:Study model-centric data curation and evaluate code model performance on benchmarks.
- Developers:Use open-source 8B code models for code generation and reasoning tasks locally or via APIs.
- Open-source community:Contribute to data curation pipelines and reproduce benchmark experiments for transparency.
Pricing Plans
Pricing information is not available yet.
Pros & Cons
✓ Pros
- ✓Open-source 8B model family (base, instruct, reasoning) tailored to code tasks.
- ✓Novel model-centric data curation: LLM-based filters capture nuanced quality signals.
- ✓Strong reported benchmark performance on SWE-bench and competitive programming tasks.
- ✓Emphasis on transparency and research reproducibility.
✗ Cons
- ✗Several site assets/pages (technical report/pdf and many subpages) return 404 or show GitHub Pages default 404 content.
- ✗Limited public documentation, downloads, or community links visible on the hosted pages.
- ✗No pricing / commercial offering information (pure open-source research focus), which may limit enterprise support pathways.
Related Articles (3)
A diffusion-based 8B code model that outperforms autoregressive and DLLM peers across major coding benchmarks.
Open-source 8B code diffusion LLMs from ByteDance Seed that outperform autoregressive peers.
Diffusion-driven pretraining with block diffusion boosts code LLMs beyond autoregressive baselines.
