Overview
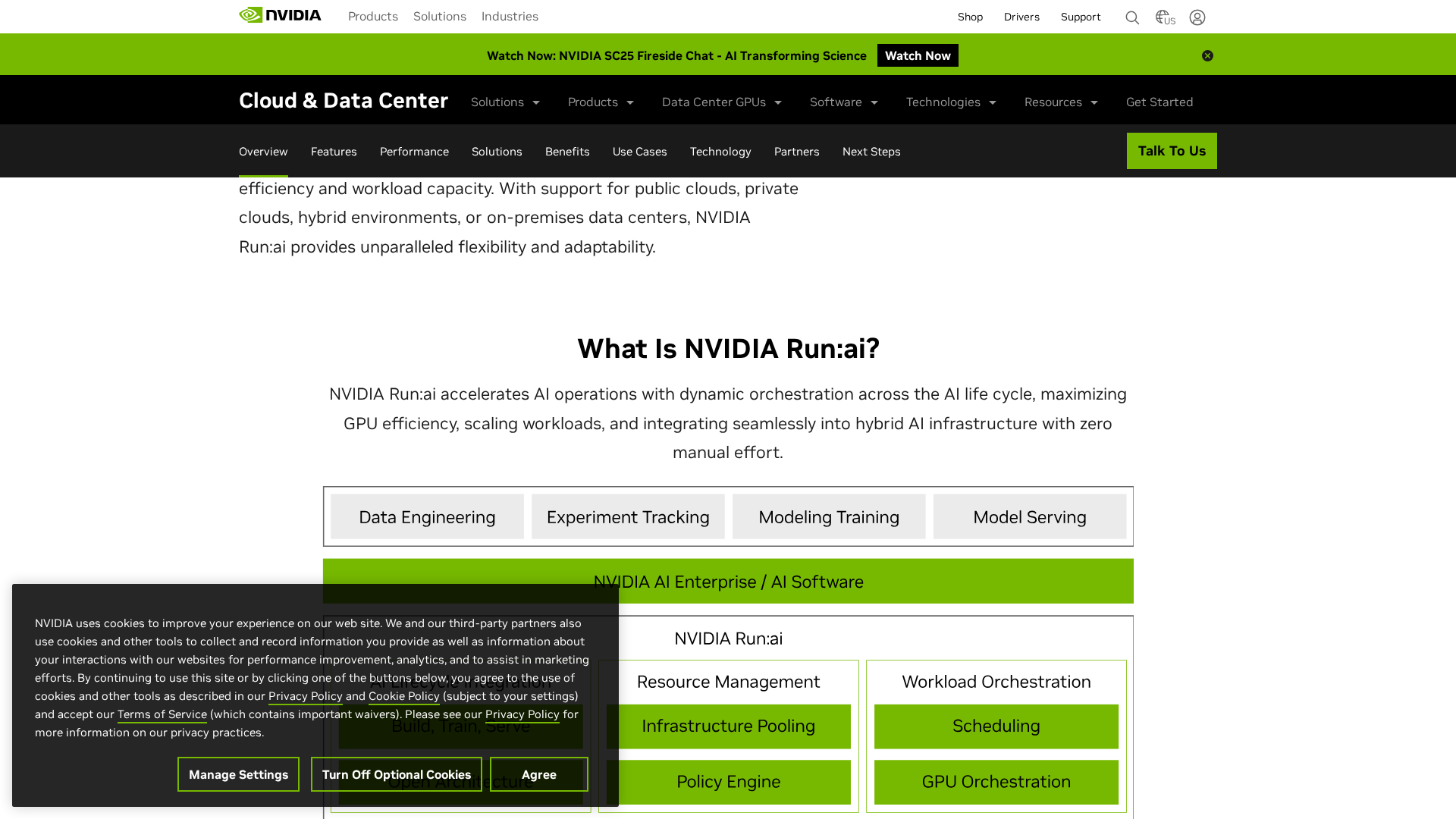
Run:ai (now shown under NVIDIA Run:ai) is a Kubernetes-native GPU orchestration and optimization platform that pools GPUs across on-prem, cloud, hybrid and multi-cloud environments to maximize GPU utilization and accelerate AI workloads across development, training and inference. Core capabilities include dynamic GPU pooling and orchestration across clusters and clouds; fractional GPU allocation with runtime resizing; scheduling optimized for AI (KAI Scheduler referenced as open-source); support for notebooks, distributed training and inference serving lifecycle; Model Streamer (SDK with C++ backend for fast model loading / streaming tensors into GPU); Grove (topology-aware serving / constrained scheduling for inference); a centralized control plane for multi-cluster management available as SaaS or self-hosted; observability with real-time and historical GPU utilization and admin dashboards; enterprise features such as RBAC, SSO and policy enforcement; and an API-first approach with UI, API and CLI. Architecture and deployment options described include a Run:ai cluster component installed in customer Kubernetes clusters (scheduling, workload execution, storage integration) and a centralized control plane (SaaS/cloud control plane or self-hosted in customer datacenter, supporting air-gapped scenarios). Documentation and whitepapers (including a Model Streamer performance benchmarks PDF) and ecosystem notes mention KAI Scheduler, Model Streamer, Grove, integrations with major ML frameworks (PyTorch, TensorFlow, etc.), storage options (S3, NFS) and partner references (DGX Cloud, NVIDIA Mission Control). Pricing is not published publicly on the site; evidence points to enterprise/quote pricing and availability via private AWS Marketplace offers. Company notes collected: founded in 2018 (founders Omri Geller and Ronen Dar); public reporting indicates Run:ai was acquired by NVIDIA (coverage around late 2024 / early 2025) and site content is integrated under NVIDIA Run:ai. Recommended next steps documented by the collector include contacting sales for pricing and private offers and preparing GPU counts, deployment model, concurrency/SLAs, integrations, and support/SLA preferences for faster quotes.
Key Features
Dynamic GPU pooling and orchestration
Pools GPUs across on‑prem, cloud, hybrid and multi‑cloud environments to maximize utilization and accelerate AI workloads.
Fractional GPU allocation and runtime resizing
Supports fractional GPU allocation and resizing of GPU fractions at runtime for more efficient sharing of GPU resources.
AI-optimized scheduling (KAI Scheduler)
Policy-driven, AI-optimized scheduling with reference to KAI Scheduler (open-source) for Kubernetes-based AI workloads.
Support for full ML lifecycle
Supports notebooks, distributed training, and inference serving lifecycle with integrations for common ML workflows.
Model Streamer
SDK with a C++ backend for fast model loading and streaming tensors into GPU; performance benchmarks available in whitepaper.
Grove (topology-aware serving)
Topology-aware serving and constrained scheduling for inference use cases.
Who Can Use This Tool?
- Enterprise ML teams:Large teams seeking centralized GPU orchestration, policy-driven scheduling and enterprise governance across clusters.
- Platform/DevOps teams:Teams managing Kubernetes clusters who need GPU pooling, fractional allocation, observability and multi-cluster control.
Pricing Plans
No public list of per-user or per-GPU pricing. Pricing is enterprise/quote-based; contact sales or use private AWS Marketplace offers.
- ✓Enterprise / quote pricing
- ✓Available via private AWS Marketplace offer (contact sales/private offer required)
- ✓SaaS or self-hosted deployment options
Pros & Cons
✓ Pros
- ✓Kubernetes-native GPU pooling across clusters and clouds
- ✓Fractional GPU allocation and runtime resizing for efficient sharing
- ✓AI-optimized scheduling (KAI Scheduler) and policy-driven orchestration
- ✓Supports notebooks, distributed training, and inference lifecycles
- ✓Model Streamer and Grove for high-performance model serving and topology-aware scheduling
- ✓Centralized multi-cluster control plane (SaaS or self-hosted) and enterprise governance features
- ✓Observability with real-time and historical GPU utilization and admin dashboards
- ✓Integrations with major ML frameworks and storage backends
✗ Cons
- ✗No public per-user or per-GPU pricing published on the site
- ✗No public free trial or self-serve pricing discovered
- ✗Pricing appears to require contacting sales or using a private AWS Marketplace offer
Compare with Alternatives
| Feature | Run:ai (NVIDIA Run:ai) | Inference.ai | FlexAI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Rating | 8.4/10 | 8.4/10 | 8.1/10 |
| GPU Pooling | Yes | Partial | Yes |
| Fractional Allocation | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Scheduler Intelligence | Yes | Partial | Yes |
| Multi-cluster Management | Yes | No | Yes |
| Model Streaming | Yes | No | No |
| Hardware & Cloud Support | On-prem cloud and multi-cloud | NVIDIA and AMD support, web-only | Cloud and BYO hardware, multicloud support |
| Observability | Yes | Partial | Yes |
| Enterprise Governance | Yes | No | Partial |
Related Articles (8)
Saudi xAI-HUMAIN launches a government-enterprise AI layer with large-scale GPU deployment and multi-year sovereignty milestones.
Saudi AI firm Humain inks multi‑party deals to scale regional AI infrastructure with Adobe, AWS, xAI and Luma AI.
Internal Nvidia emails reveal a 'fundamental disconnect' with clients as it scales AI enterprise software into regulated industries.

Nokia launches 7220 IXR-H6 switches with 102.4 Tb/s throughput and AI-enabled EDA AIOps to boost AI data centers.
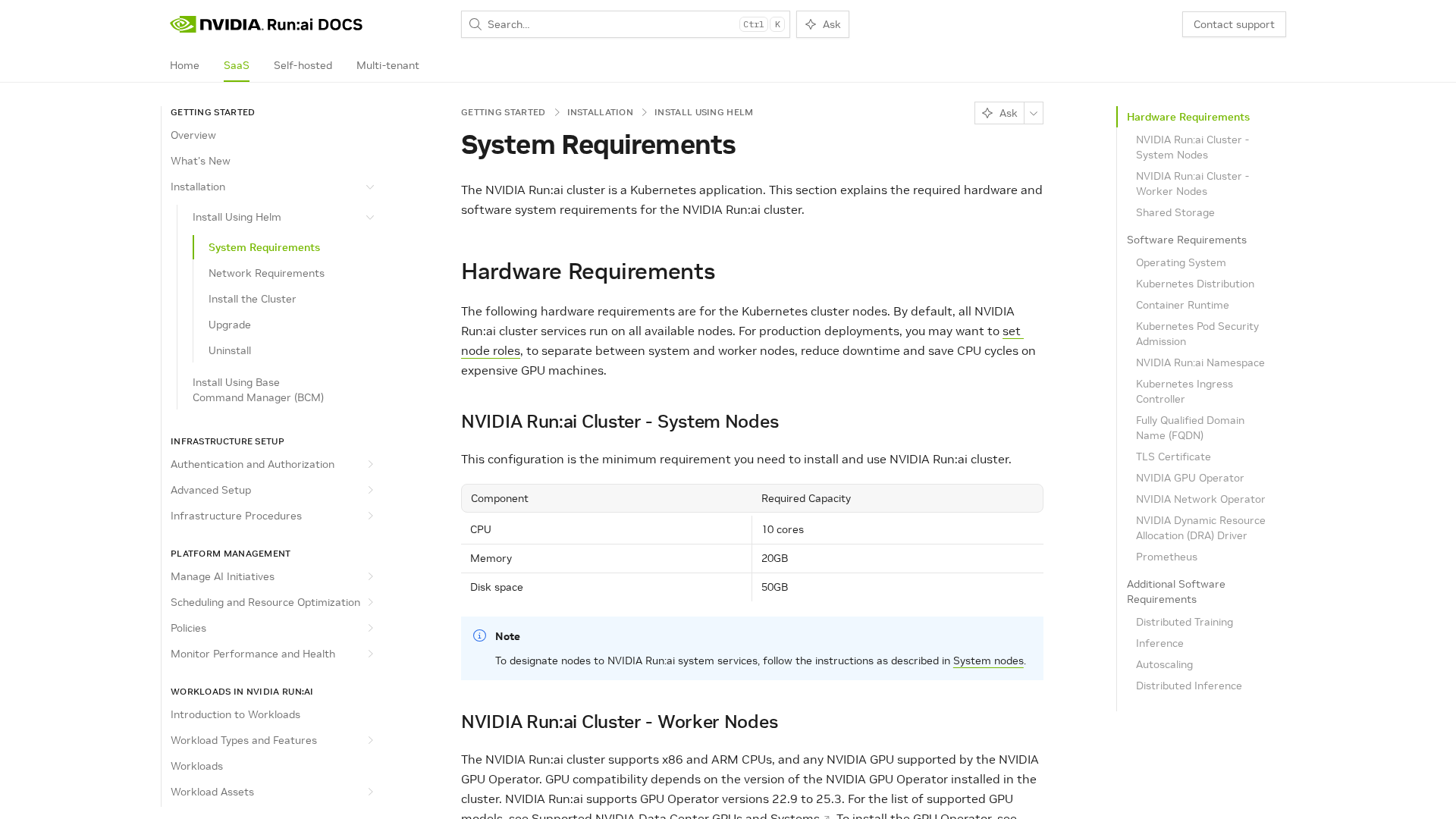
A comprehensive guide to hardware, software, and deployment requirements for NVIDIA Run:ai on Kubernetes.
