Topic Overview
Generative AI coding assistants and models now power everyday development workflows, from inline completions to autonomous agentic tasks. This topic examines how leading systems — Claude Opus 4.5 and ChatGPT as generalist/code-capable models, GitHub Copilot (IDE-integrated pair programmer with chat and agent workflows), Amazon CodeWhisperer (inline suggestions within the Amazon Q Developer experience), and specialist/code-first models like Code Llama and Stable Code — differ in capabilities and deployment trade-offs. Relevance in 2026 stems from three converging trends: wider adoption of instruction‑tuned, code‑aware LLMs; a push for local/self‑hosted and edge‑ready models to address latency, privacy, and IP concerns (e.g., Tabby, Stable Code); and the rise of agentic development environments that chain model actions into developer workflows (Warp, Blackbox.ai). Complementary tools — CodeGeeX, Bito (PR and review automation), and other codebase‑aware assistants — emphasize codebase context, review automation, and reproducible fixes. Key comparison axes include correctness and hallucination rates, context‑window and cross‑repo awareness, latency, IDE and CI/CD integrations, licensing and security constraints, and support for autonomous tasks (test generation, bug fixes, pull request automation). Practical trade‑offs matter: cloud-hosted scalable models tend to offer broader knowledge and managed safety, while self‑hosted/open models give control over data and compliance. Evaluations should therefore consider real project needs (team size, codebase sensitivity, language stack, CI integration) rather than raw model benchmarks. This topic helps developers and managers choose between off‑the‑shelf services and self‑hosted code models, and understand how these tools fit into modern development pipelines.
Tool Rankings – Top 6
An AI pair programmer that gives code completions, chat help, and autonomous agent workflows across editors, theterminal

AI-based coding assistant for code generation and completion (open-source model and VS Code extension).
AI-driven coding assistant (now integrated with/rolling into Amazon Q Developer) that provides inline code suggestions,

Edge-ready code language models for fast, private, and instruction‑tuned code completion.
All-in-one AI coding agent and developer platform offering chat, code generation, debugging, IDE plugins, and enterprise
.avif)
Open-source, self-hosted AI coding assistant with IDE extensions, model serving, and local-first/cloud deployment.
Latest Articles (45)
Meta may partner with Sify to lease a 500 MW Vishakhapatnam data center in a Rs 15,266 crore project linked to the Waterworth subsea cable.
Meta and Sify plan a 500 MW hyperscale data center in Visakhapatnam with the Waterworth subsea cable landing.
Learn how Builder’s Stripe integration enables secure, in-app payments and streamlined monetization.
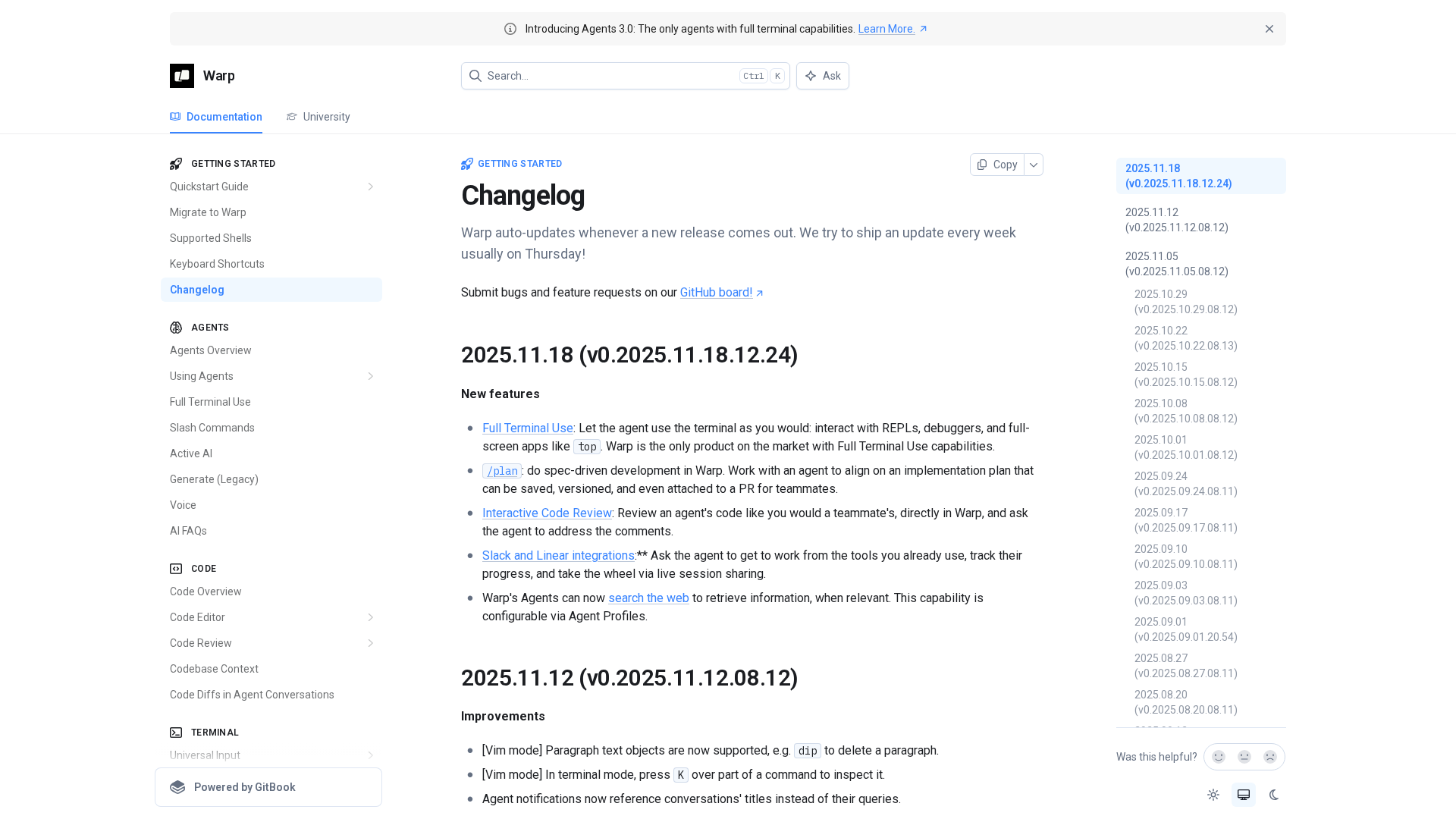
Warp’s weekly changelog highlights new Agent Mode features, improved stability, and cross-platform enhancements.
Overview of TabbyML's Tabby, a self-hosted AI coding assistant, and its place in a growing ecosystem of local-first AI tools.