Topic Overview
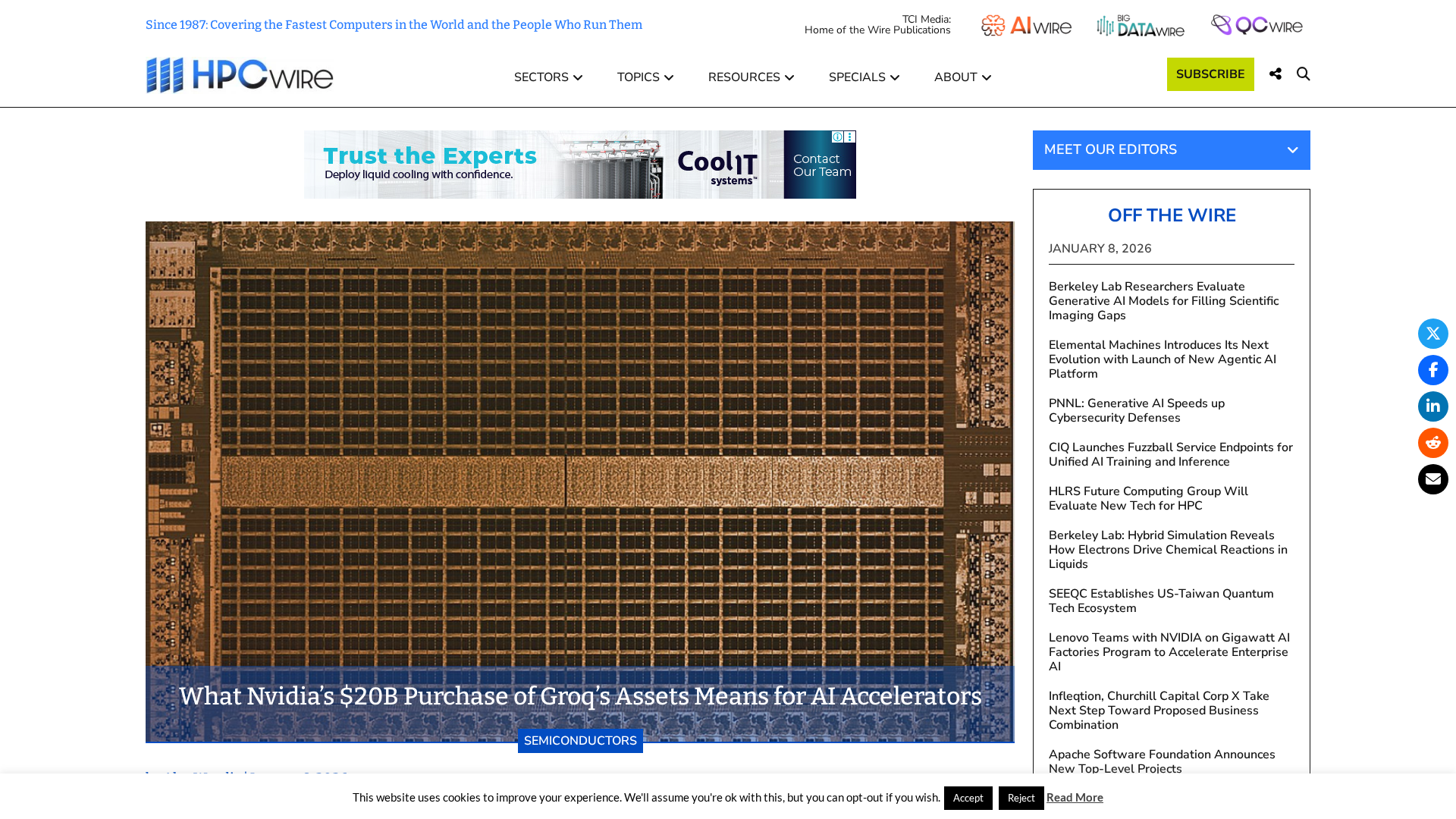
This topic examines the evolving landscape of AI accelerators across on‑device and data‑center environments and how hardware, software, and infrastructure choices affect next‑generation workloads (LLMs, multimodal vision, real‑time inference). Hardware examples include vendor accelerators such as NVIDIA Rubin, Intel Panther Lake, and cloud chips like AWS Trainium and Inferentia; alongside boutique silicon and stack vendors (e.g., Rebellions.ai) focused on energy‑efficient inference. Relevance in 2026 arises from three converging trends: model scale and multimodality driving demand for specialized compute; tighter cost and energy constraints that prioritize inference efficiency; and regulatory/data‑locality pressures pushing workloads to the edge or decentralized infrastructure. Edge AI Vision Platforms need compact, low‑latency inference engines; Decentralized AI Infrastructure (e.g., initiatives like Tensorplex Labs) explores distributed hosting, staking, and governance; and AI Data Platforms must integrate model‑aware data pipelines for training and fine‑tuning. Software and model ecosystems matter: models such as Code Llama illustrate domain‑specialized workloads that influence accelerator selection, while developer tooling like Windsurf (agentic IDEs) emphasizes multi‑model integration and live feedback, requiring predictable latency and standardized runtimes. Industry consolidation and vendor integrations—seen in acquisitions and shifting vendor stacks—underscore the importance of software–hardware co‑design and portable runtimes. Choosing between on‑device and data‑center accelerators depends on workload profile (training vs inference, latency, privacy), cost/energy targets, and available software tooling. The practical direction for practitioners is hybrid: pair cloud training accelerators with edge‑optimized inference silicon, and prioritize toolchains that streamline model optimization and deployment across both domains.
Tool Rankings – Top 5
Code-specialized Llama family from Meta optimized for code generation, completion, and code-aware natural-language tasks
AI-native IDE and agentic coding platform (Windsurf Editor) with Cascade agents, live previews, and multi-model support.
Energy-efficient AI inference accelerators and software for hyperscale data centers.

Site audit of deci.ai showing NVIDIA takeover after May 2024 acquisition and absence of Deci-branded pricing.
Open-source, decentralized AI infrastructure combining model development with blockchain/DeFi primitives (staking, cross
Latest Articles (29)
How AI agents can automate and secure decentralized identity verification on blockchain-enabled systems.
AWS commits $50B to expand AI/HPC capacity for U.S. government, adding 1.3GW compute across GovCloud regions.
Passage cuts GPU cloud costs by up to 70% using Akash's open marketplace, enabling immersive Unreal Engine 5 events.
ProteanTecs expands in Japan with a new office and Noritaka Kojima as GM Country Manager.
Windsurf unveils SWE-1.5 and a bold plan for affordable, enterprise-ready AI coding.