Topic Overview
Predictive maintenance & industrial AI systems built on large language models (LLMs) combine natural‑language reasoning, retrieval-augmented workflows, and agent orchestration with traditional sensor analytics and edge vision. This topic compares LLM-centric stacks — typified by collaborations that pair conversational/developer LLMs (Anthropic’s Claude family) with enterprise asset-management and field-service platforms (e.g., IFS-style solutions) — against incumbent rule-based or classical ML solutions used for condition monitoring and maintenance planning. Relevance (as of 2025-12-03): organizations are operationalizing LLMs into industrial workflows to accelerate fault diagnosis, convert manuals and maintenance logs into searchable document agents, and automate multi-step remediation. This trend raises practical tradeoffs: improved natural language interfaces and faster root-cause hypotheses versus new needs for data governance, model evaluation, latency control at the edge, and safety validation. Key tooling and roles: - Claude (Anthropic): conversational and developer LLMs for analysis, troubleshooting dialogs, and human–AI collaboration. - IBM watsonx Assistant: enterprise virtual agents and multi-agent orchestrations for production-grade automation and no-code deployment. - LlamaIndex: converts unstructured manuals, SOPs, and sensor histories into retrieval-augmented document agents for explainable RAG workflows. - LangChain: engineering frameworks and orchestration primitives to build, test, and deploy agentic LLM applications across services and devices. - KaneAI: GenAI-native testing agent to create and evolve end‑to‑end tests that validate workflows, APIs, and UI interactions. Where they differ from traditional solutions: LLM stacks emphasize RAG, conversational troubleshooting, and multi-agent orchestration; traditional systems prioritize deterministic rules, validated statistical models, and tightly controlled on‑prem deployments. Practical deployments tend to be hybrid: edge AI vision platforms and AI data platforms handle low‑latency inference and governed telemetry, while LLMs deliver reasoning, summarization, and orchestration. Key considerations include latency, explainability, testability, and compliance when replacing or augmenting legacy predictive‑maintenance workflows.
Tool Rankings – Top 5
Anthropic's Claude family: conversational and developer AI assistants for research, writing, code, and analysis.

KaneAI is a GenAI-native testing agent that plans, writes, and evolves end-to-end tests using natural language.
Engineering platform and open-source frameworks to build, test, and deploy reliable AI agents.
Enterprise virtual agents and AI assistants built with watsonx LLMs for no-code and developer-driven automation.

Developer-focused platform to build AI document agents, orchestrate workflows, and scale RAG across enterprises.
Latest Articles (66)

A comprehensive comparison and buying guide to 14 AI governance tools for 2025, with criteria and vendor-specific strengths.
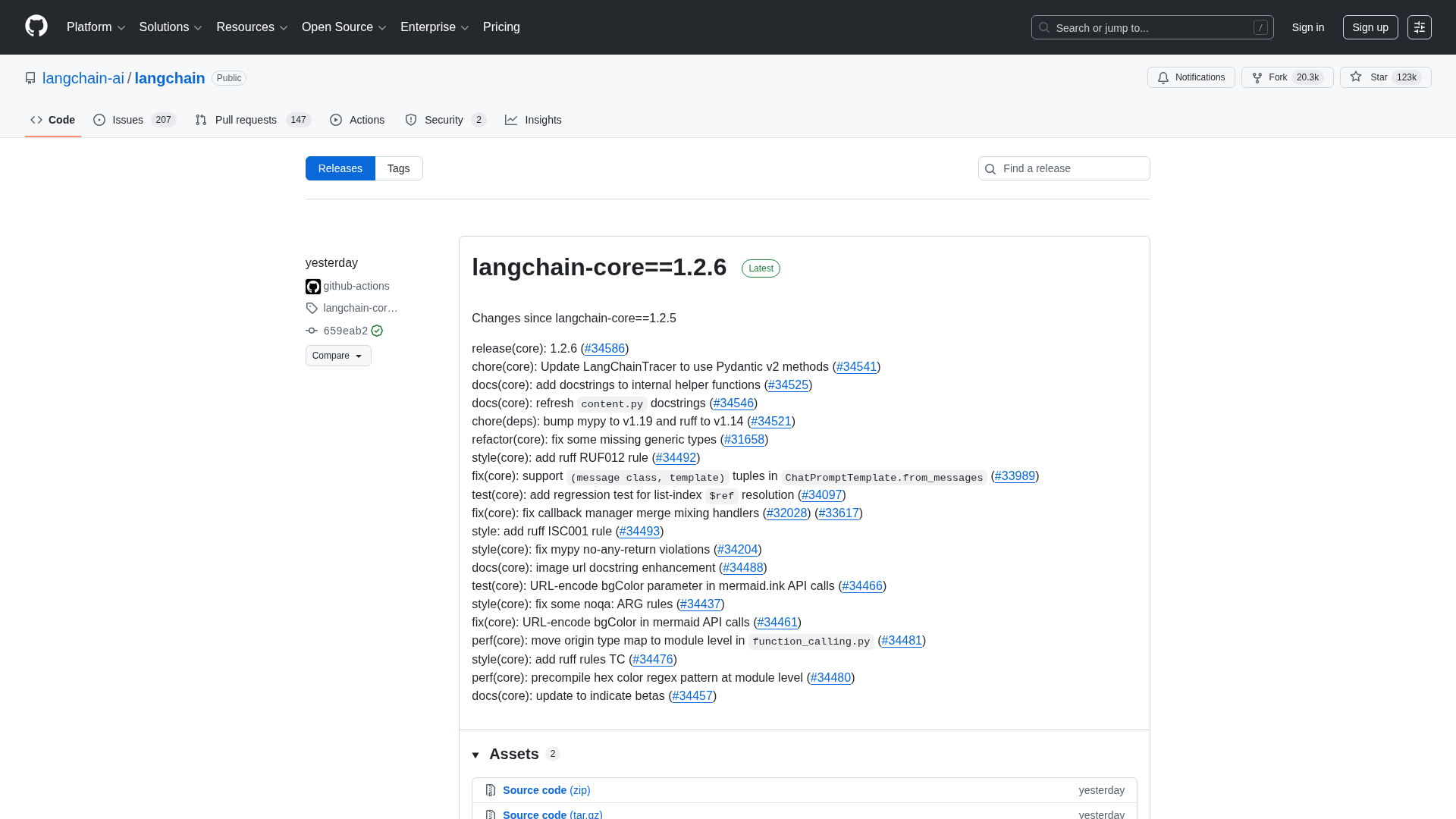
A comprehensive LangChain releases roundup detailing Core 1.2.6 and interconnected updates across XAI, OpenAI, Classic, and tests.
Content missing from the provided source; please supply the article text for full analysis.
TTMS shows how AI4 E-learning turns complex manufacturing docs into fast, on-the-job microlearning with governance and ROI guidance.
A centralized LambdaTest docs hub for cross-browser testing, automation, and AI-powered insights.
