Topic Overview
This topic covers multi-agent AI frameworks and platforms designed to automate and support healthcare and clinical workflows — from multidisciplinary decision support to documentation, patient triage, and contact‑center interactions. As of 2026, momentum has shifted toward production-grade orchestration: developer-first SDKs for building agent chains, no-code/low-code platforms for enterprise adoption, and secure integrations into clinician collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams. Key components include agent frameworks such as LangChain (developer SDKs and a commercial platform for building, observing, and deploying LLM-powered agents) and AutoGen-style integrations for coordinating multiple specialized agents; enterprise assistants such as IBM watsonx Assistant that enable no-code and developer-driven multi-agent orchestrations; and platforms like StackAI that lower the barrier with end-to-end governance. Supporting services focus on prompt/version management and observability (Pezzo), data curation for efficient model training (DatologyAI), document-centric Q&A for literature and records (PDF.ai), and conversational LLMs (Anthropic’s Claude family) for analysis and summarization. Notion and Observe.AI surface knowledge and real‑time conversational intelligence into workflows, while TrustedMDT and Teams-based agents represent the operational patterns that bring multi-agent outputs into clinician multidisciplinary-team workflows and meeting/chat contexts. Practical priorities in 2026 include EHR and Teams integration, traceability and governance, on‑prem or enterprise LLM deployment for PHI protection, RAG and vector-store pipelines for clinical knowledge, and observability to audit agent decisions. Together these tools and platforms form a stack for building clinically focused, governed multi-agent systems that emphasize safety, interoperability, and measurable workflow impact rather than one-off experiments.
Tool Rankings – Top 6
An open-source framework and platform to build, observe, and deploy reliable AI agents.
Enterprise virtual agents and AI assistants built with watsonx LLMs for no-code and developer-driven automation.

End-to-end no-code/low-code enterprise platform for building, deploying, and governing AI agents that automate work onun

Developer-first platform to build, test, monitor, and ship AI features quickly while optimizing cost and performance.

Data-curation-as-a-service to train models faster, better, and smaller.
Chat with your PDFs using AI to get instant answers, summaries, and key insights.
Latest Articles (92)
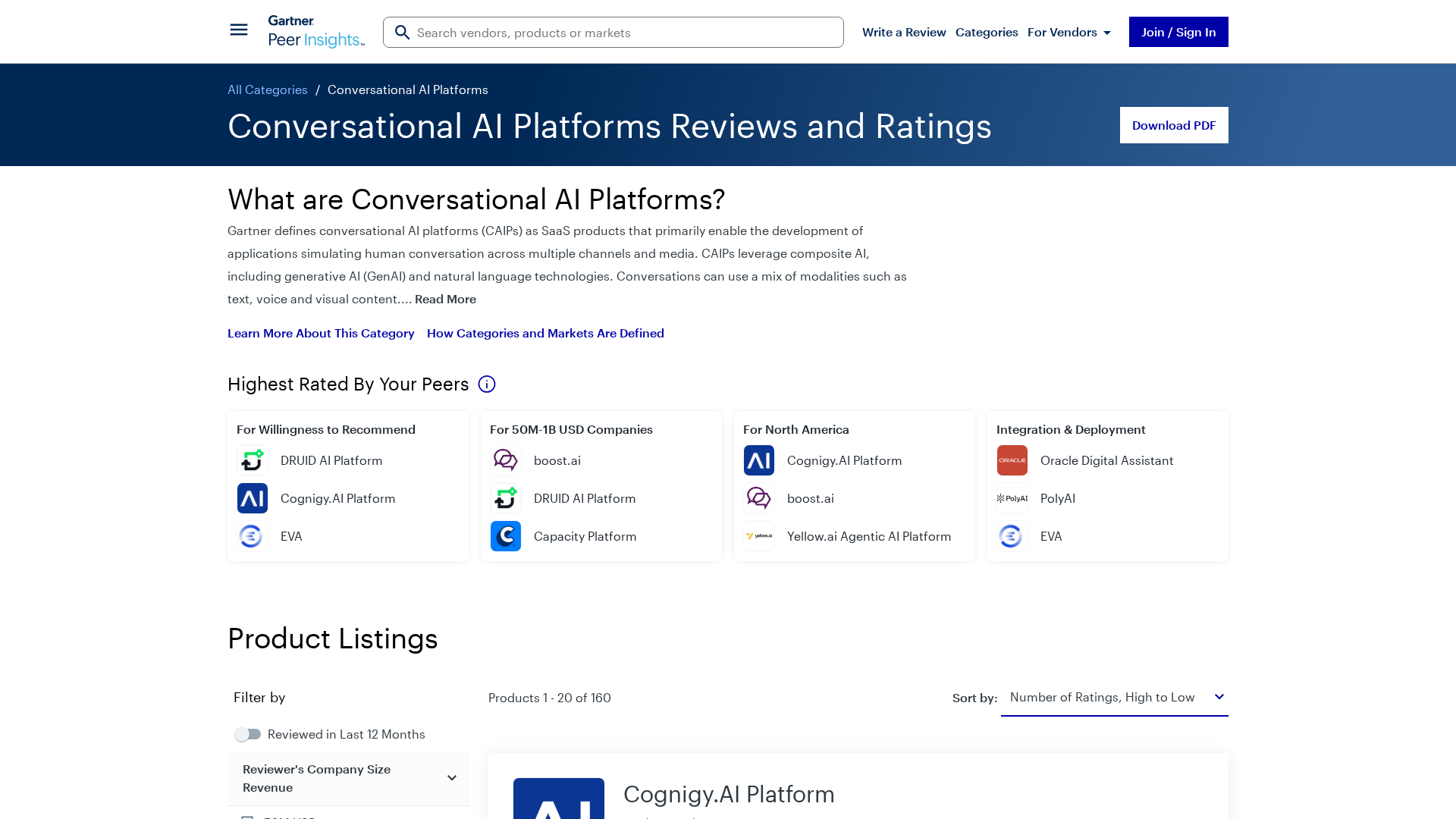
Gartner’s market view on conversational AI platforms, outlining trends, vendors, and buyer guidance.

A comprehensive comparison and buying guide to 14 AI governance tools for 2025, with criteria and vendor-specific strengths.
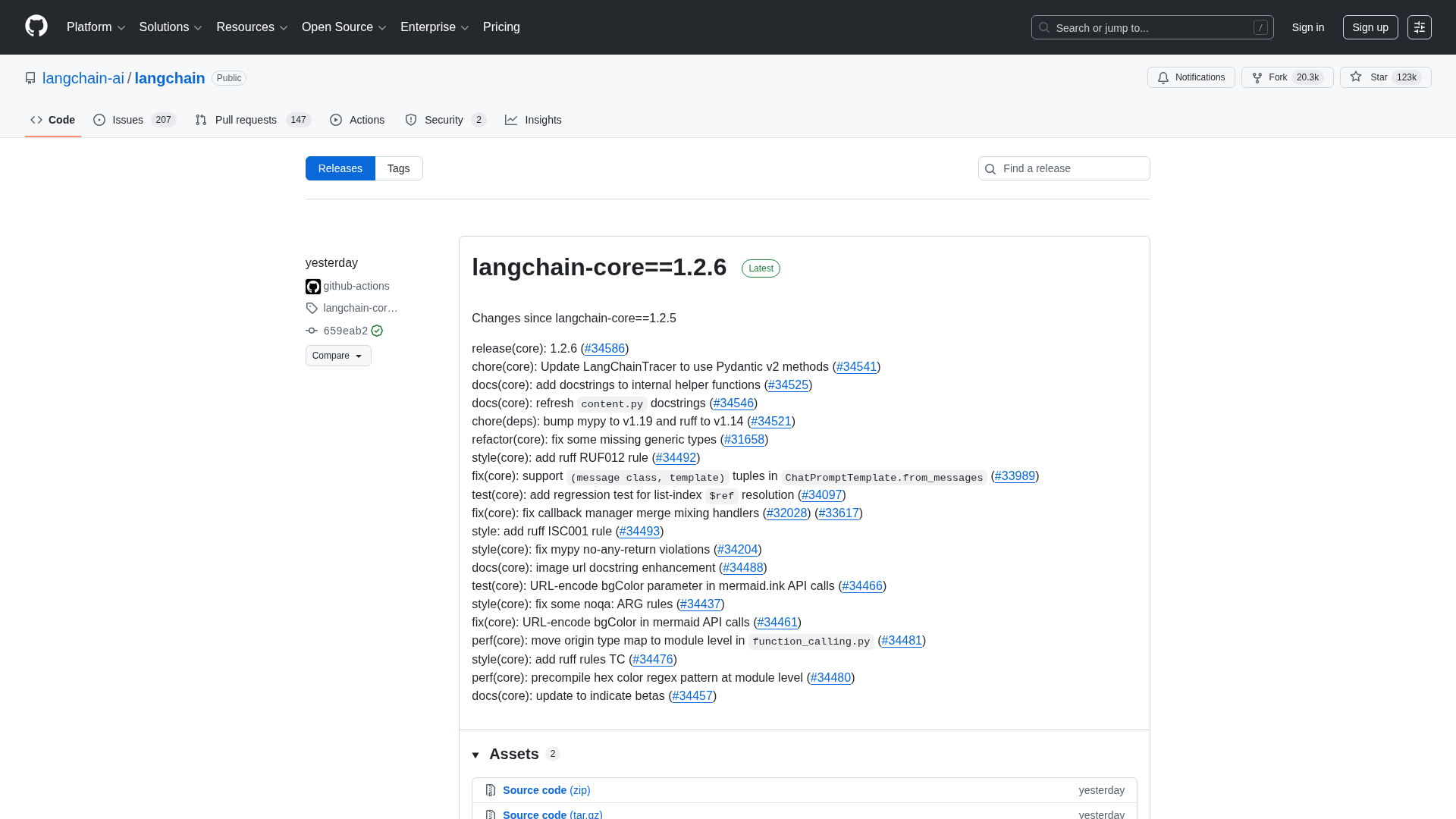
A comprehensive LangChain releases roundup detailing Core 1.2.6 and interconnected updates across XAI, OpenAI, Classic, and tests.
A reproducible bug where LangGraph with Gemini ignores tool results when a PDF is provided, even though the tool call succeeds.
A CLI tool to pull LangSmith traces and threads directly into your terminal for fast debugging and automation.
