Topic Overview
This topic compares contemporary frameworks for LLM inference and fine‑tuning — from runtime “fabrics” and enterprise inference servers to managed fine‑tuning platforms, agent frameworks, and purpose‑built accelerators — and explains what to evaluate when deploying production GenAI. As of late 2025, teams balance latency, throughput, observability, data governance, and energy efficiency while integrating agent orchestration and automated testing into CI/CD. Key solution types include: managed platforms like OpenPipe for collecting request/response logs, preparing datasets, fine‑tuning models, and hosting optimized inference; engineering and agent frameworks such as LangChain and LlamaIndex that focus on building, debugging, and deploying agentic and RAG workflows; developer environments like Warp that embed agents into dev flows; hardware and stack vendors like Rebellions.ai that supply energy‑efficient inference accelerators and server software; and experimental infrastructure projects such as Tensorplex Labs exploring decentralized model development. Tether QVAC Fabric and Red Hat AI Inference Server are representative of two approaches practitioners will compare: fabric‑style runtimes that prioritize flexible orchestration across heterogeneous hardware, and enterprise inference servers that emphasize stability, integrations, and platform governance. Key evaluation dimensions are throughput/latency, model update and fine‑tuning pipelines, observability and test automation for GenAI (functional, safety, and regression tests), on‑prem vs cloud tradeoffs for data privacy, and hardware compatibility including accelerator stacks. This comparison is timely because the market is maturing from point solutions to integrated toolchains linking data capture, fine‑tuning, agent orchestration, and automated evaluation. Teams selecting a stack should map requirements (agents, RAG, compliance, cost, and energy) to these tool categories and prioritize interoperability and measurable test automation.
Tool Rankings – Top 6

Managed platform to collect LLM interaction data, fine-tune models, evaluate them, and host optimized inference.
Engineering platform and open-source frameworks to build, test, and deploy reliable AI agents.

Developer-focused platform to build AI document agents, orchestrate workflows, and scale RAG across enterprises.

Agentic Development Environment (ADE) — a modern terminal + IDE with built-in AI agents to accelerate developer flows.
Energy-efficient AI inference accelerators and software for hyperscale data centers.
Open-source, decentralized AI infrastructure combining model development with blockchain/DeFi primitives (staking, cross
Latest Articles (65)
A comprehensive LangChain releases roundup detailing Core 1.2.6 and interconnected updates across XAI, OpenAI, Classic, and tests.
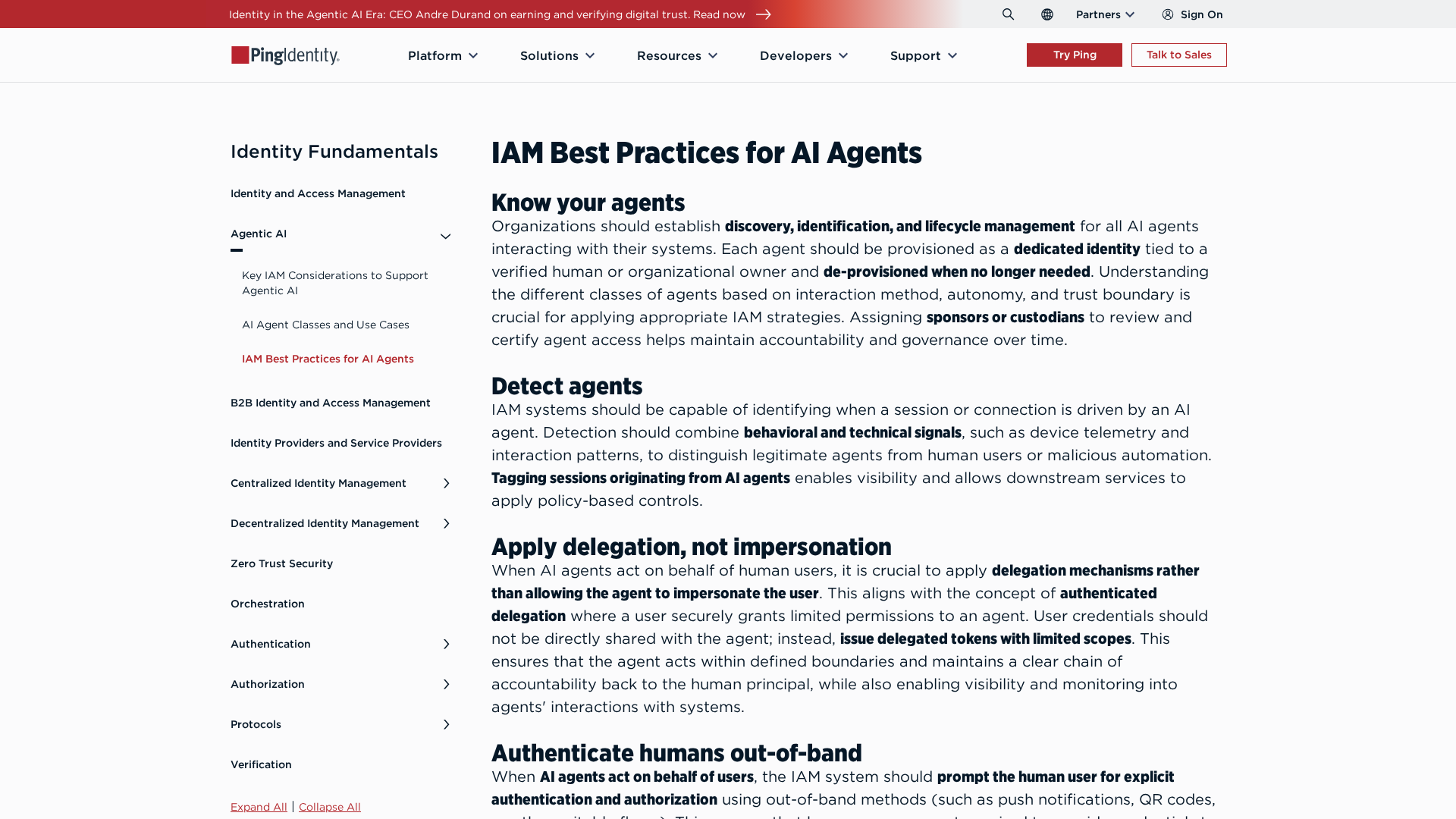
Best-practices for securing AI agents with identity management, delegated access, least privilege, and human oversight.

Cannot access the article content due to an access-denied error, preventing summarization.
AWS commits $50B to expand AI/HPC capacity for U.S. government, adding 1.3GW compute across GovCloud regions.
How AI agents can automate and secure decentralized identity verification on blockchain-enabled systems.