Topic Overview
This topic covers how vector databases and memory systems are used to give large language models (LLMs) persistent, retrievable context — from session-level short-term memory to enterprise-scale long-term knowledge stores. Vector databases such as Pinecone, Milvus and Weaviate provide the underlying semantic indexes and metadata filtering that retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), conversational agents, and enterprise search rely on. They differ along lines of managed vs. self-hosted deployments, index algorithms (HNSW, IVF, quantized indexes), and operational features like streaming ingestion, vector compression, and hybrid keyword+semantic search. Why it matters in late 2025: production LLM applications increasingly need reliable, low-latency access to evolving corpora (documents, logs, user profiles, code) while meeting governance, privacy and cost constraints. Long-term memory patterns — memory condensation, TTL/decay, versioned snapshots, and selective retrieval policies — are now standard design choices for agent frameworks and developer platforms. Tooling around these stores is maturing: LangChain and similar frameworks provide engineering primitives and stateful graphs for integrating vector stores into agent workflows; no-code platforms like MindStudio let product teams design and operate memory-enabled agents without heavy engineering effort; AutoGPT-style runtimes and developer platforms such as GPTConsole focus on lifecycle, chaining, and memory orchestration. Enterprise-focused assistants (e.g., Tabnine for code) emphasize private deployments and governance tied to vector storage. Practitioners should evaluate index scalability, multimodal vector support, ingestion latency, metadata/query flexibility, and integration with agent frameworks and governance tooling when choosing a long-term memory solution for LLMs.
Tool Rankings – Top 5
Engineering platform and open-source frameworks to build, test, and deploy reliable AI agents.

No-code/low-code visual platform to design, test, deploy, and operate AI agents rapidly, with enterprise controls and a
Platform to build, deploy and run autonomous AI agents and automation workflows (self-hosted or cloud-hosted).

Developer-focused platform (SDK, API, CLI, web) to create, share and monetize production-ready AI agents.
Enterprise-focused AI coding assistant emphasizing private/self-hosted deployments, governance, and context-aware code.
Latest Articles (30)
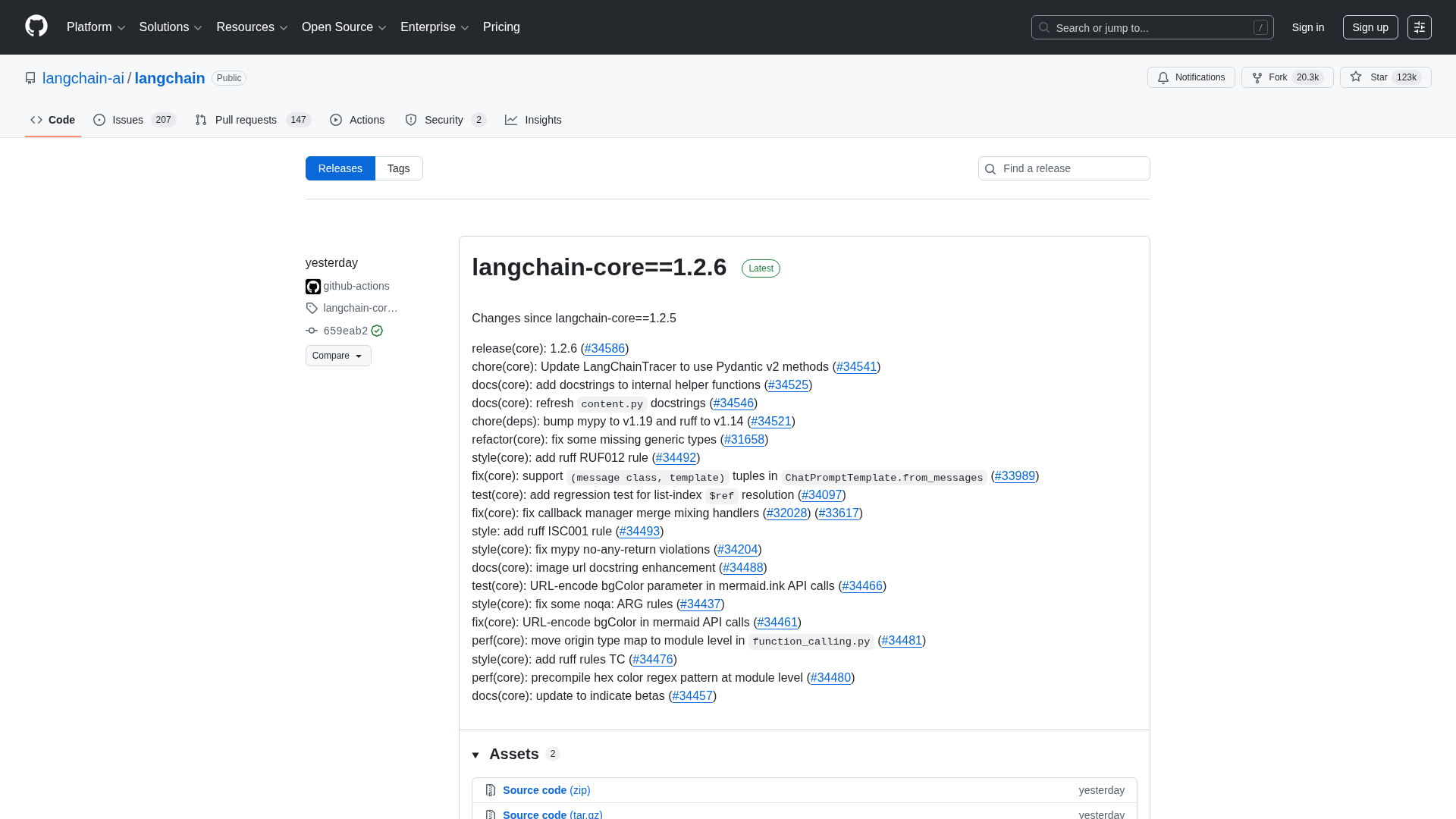
A comprehensive LangChain releases roundup detailing Core 1.2.6 and interconnected updates across XAI, OpenAI, Classic, and tests.

Cannot access the article content due to an access-denied error, preventing summarization.
A quick preview of POE-POE's pros and cons as seen in G2 reviews.
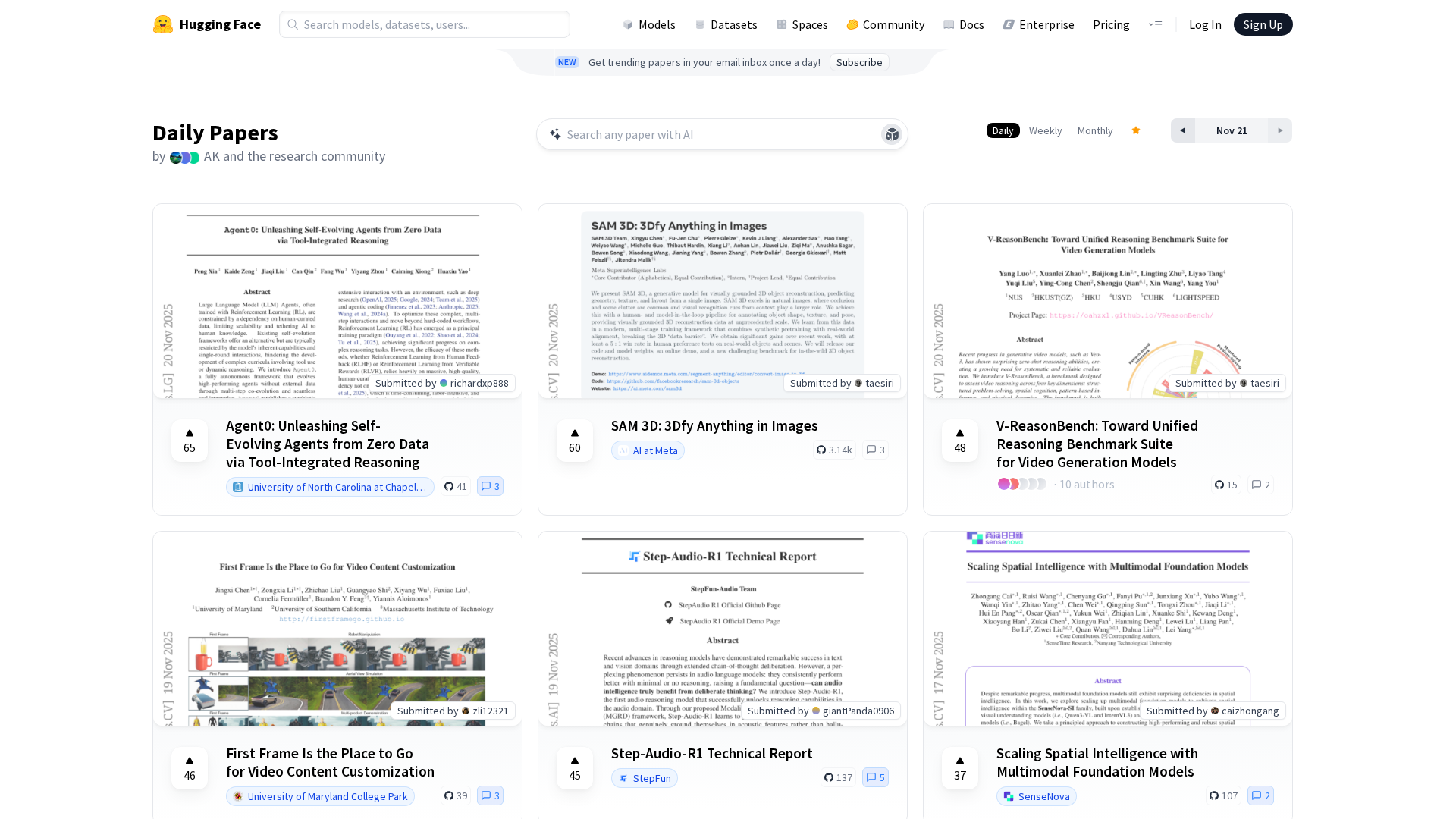
Get daily, curated trending ML papers delivered straight to your inbox.
Dell unveils 20+ advancements to its AI Factory at SC25, boosting automation, GPU-dense hardware, storage and services for faster, safer enterprise AI.
