Topic Overview
This topic covers the practical tradeoffs and capabilities of leading cloud GPU and AI infrastructure providers for model training and inference as of 2026. It explains how hardware vendors (NVIDIA) and cloud providers (AWS, CoreWeave, Unicorne) differ in performance, software stacks, pricing models, and deployment patterns—information teams need to pick infrastructure that matches model size, latency and cost targets, and data governance requirements. NVIDIA remains central for high‑performance training and inference through its H100/A100 family and software ecosystem (CUDA, cuDNN, Triton), while AWS complements NVIDIA hardware with a broad accelerator portfolio (EC2 GPU instances, Trainium and Inferentia chips) plus managed services such as SageMaker. CoreWeave exemplifies GPU‑native cloud providers that prioritize flexible, on‑demand GPU capacity and competitive pricing for large‑scale training and inference. Unicorne represents smaller or emerging specialized providers and marketplaces that focus on managed GPU clusters, spot capacity, and decentralized access patterns—useful where cost, locality, or data sovereignty drive decisions. The overview also links infrastructure choices to AI data platforms and orchestration tooling: frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex are commonly used to build retrieval‑augmented generation (RAG) pipelines and agents that rely on consistent inference latency and colocated data. Developer tools such as GitHub Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer (Amazon Q Developer), and Tabnine illustrate downstream services whose performance and cost depend directly on infrastructure selection. Key trends for 2026 include hardware specialization, model quantization and mixed‑precision optimization, spot/marketplace capacity for cost savings, and an increasing emphasis on decentralized and data‑aware deployment strategies. The result: pick infrastructure based on workload profile, integration needs (RAG, agent frameworks), and governance constraints rather than on headline performance alone.
Tool Rankings – Top 5
An open-source framework and platform to build, observe, and deploy reliable AI agents.

Developer-focused platform to build AI document agents, orchestrate workflows, and scale RAG across enterprises.
AI-driven coding assistant (now integrated with/rolling into Amazon Q Developer) that provides inline code suggestions,
An AI pair programmer that gives code completions, chat help, and autonomous agent workflows across editors, theterminal
Enterprise-focused AI coding assistant emphasizing private/self-hosted deployments, governance, and context-aware code.
Latest Articles (33)
A comprehensive LangChain releases roundup detailing Core 1.2.6 and interconnected updates across XAI, OpenAI, Classic, and tests.
A reproducible bug where LangGraph with Gemini ignores tool results when a PDF is provided, even though the tool call succeeds.
A CLI tool to pull LangSmith traces and threads directly into your terminal for fast debugging and automation.
A practical guide to debugging deep agents with LangSmith using tracing, Polly AI analysis, and the LangSmith Fetch CLI.
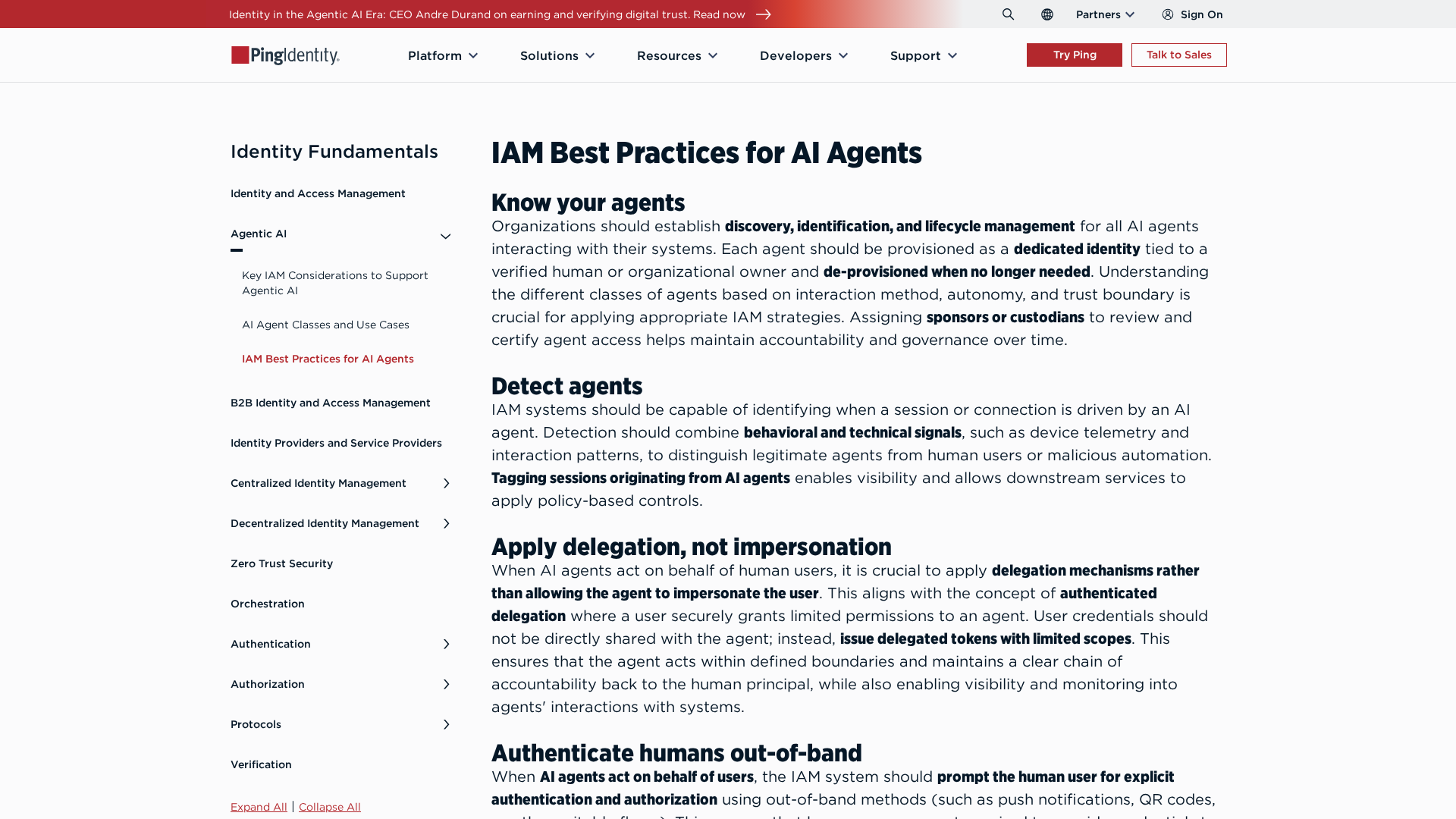
Best-practices for securing AI agents with identity management, delegated access, least privilege, and human oversight.
